Give us a call at 800-971-5369
Give us a call at
800-971-5369

What is a power chair? A power chair, commonly known as an electric wheelchair, is a mobility device that provides independence for individuals with limited movement. It's propelled by an electric motor rather than manual power, making it an essential tool for those with severe disabilities or long-term mobility issues. The chairs often come with a variety of features that cater to the specific needs of the user, such as customizable seating, control systems, and varying levels of support and mobility.
These versatile chairs are designed to improve the quality of life by enabling users to navigate various environments with ease. The maneuverability of power chairs allows users to perform daily activities more effectively, as they can move around obstacles and tight spaces. Different models accommodate various body types and disabilities, ensuring that users find a suitable match for their individual needs.
SHOP OUR BRILLIANT SELECTION OF POWER WHEELCHAIRS HERE
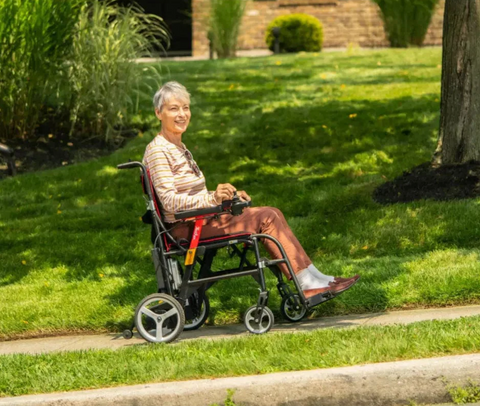

Power chairs, often known as power wheelchairs, provide mobility assistance to individuals facing challenges with walking due to various conditions. They offer a blend of autonomy and technological innovation.
What is a power wheelchair? A power chair is a motorized device designed to assist individuals with mobility impairments. Unlike traditional manual wheelchairs, power chairs are propelled by electric motors and controlled by a joystick or alternative input device. They serve two essential functions: enhancing personal mobility and reducing the physical strain of manual propulsion. Power chairs often come equipped with rechargeable batteries and provide users with the freedom to move independently.
Power chairs vary significantly in design and function to cater to the diverse needs of their users. The following list highlights the primary categories:
Each type of power chair is tailored to different user needs, from indoor maneuverability to outdoor durability.

SHOP LIGHTWEIGHT POWER CHAIRS HERE
Power chairs, also known as electric wheelchairs or power wheelchairs, offer mobility solutions with various customizable features, control systems, and battery technologies. They cater to different user needs, from basic maneuverability to advanced capabilities.
Power chairs come with a range of customizable options to enhance user comfort and meet individual requirements. Seat size, cushion type, and backrest support can be tailored to the user's body dimensions and specific needs. Adjustable armrests and leg rests ensure proper positioning and support. Furthermore, power chairs may offer various wheel types fit for different terrains, and color choices for personal aesthetics.
The control system is a crucial aspect of power chairs, dictating their maneuverability. Users typically manage their chairs using a joystick, which can be mounted on the left or right side to accommodate dominant hand usage. For those with limited hand mobility, alternative controls such as:
allow for precise navigation. Some models are equipped with smart technology options like Bluetooth connectivity to interface with other devices.
The battery system is the powerhouse of a power chair, determining how far and how long it can go between charges. Lead-acid, gel cell, and lithium-ion batteries are commonly used, each with different capacities and maintenance requirements.
Average battery life typically ranges from 8 to 20 miles per charge, but it highly depends on the chair's use, weight load, and terrain. Most power chairs come with a standard onboard charger, and charging is as simple as plugging the chair into a standard electrical outlet. Charge times can vary, usually taking between 2 to 12 hours to fully recharge.
SHOP OUR PORTABLE ELECTRIC WHEELCHAIRS

A power wheelchair, commonly known as a power chair, offers users with mobility challenges the ability to move with greater ease and less reliance on others. This enhances users' lifestyle by providing them with a level of independence that manual wheelchairs might not offer.
Power chairs are equipped with electric motors, enabling users to traverse longer distances without physical fatigue. They come with a variety of control systems, like joysticks or touchpads, which are beneficial for individuals with limited upper body strength or dexterity. These chairs often allow for navigation in tighter spaces, making them suitable for both indoor and outdoor use.
The design of power chairs prioritizes comfort with options for customizable seating, such as contoured or pressure-relieving cushions. They accommodate various postural needs and are adjustable to fit different body types, enhancing the overall comfort for users.
Power chairs are also an essential tool for accessing environments that might be otherwise difficult to navigate, such as ramps or elevators. They often feature durable wheels and suspension systems to tackle a variety of surfaces and small obstacles.
Selecting the right power wheelchair, commonly referred to as a power chair, involves careful consideration of individual needs and an evaluation process to ensure the best fit for the user's lifestyle.
Size and Weight: The user's physical dimensions are critical. A power chair should accommodate their height and weight comfortably. Look for models with adjustable features for a custom fit.
Indoor vs. Outdoor Use: The environment where the power chair will be used influences the choice.
Controls: The user's ability to operate a joystick or alternative control system should be assessed. Ensure they are intuitive and within easy reach.
SHOP OUR BRILLIANT SELECTION OF POWER WHEELCHAIRS HERE
Professional Assessment: A health care professional, such as an occupational therapist, should evaluate the user's mobility needs. They will identify the appropriate features – such as tilt, recline, or elevated seating.
| Feature | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Tilt-in-space | Pressure relief, comfort |
| Recline | Stretching, relaxation |
| Elevating leg rests | Circulation improvement |
| Adjustable arm rests | Entry, exit and comfort adjustment |
Hands-On Trial: Before purchasing, users should test various models to check for comfort and assess how well the power chair meets their needs. Testing should mimic typical daily activities to get a realistic feel for functionality and performance.
Battery Care: A power wheelchair's battery is critical for its operation. It is typically recommended to charge the battery after each use to ensure it's always ready. Batteries should be charged in a well-ventilated area, following the manufacturer's instructions. Longevity is enhanced by avoiding deep discharges and not leaving the battery in a discharged state for extended periods.
Cleaning: To maintain the power chair in good condition, it should be cleaned regularly. Use a damp cloth to wipe the surfaces and avoid harsh chemicals that could damage the chair's components. The seating and backrest may have specific cleaning instructions based on the materials they are made from.
Tire Inspection: Regularly check the tires for wear and tear. Pneumatic tires require consistent pressure checks to maintain the recommended level. Solid tires, while not requiring inflation, should be examined for any damage that could impair mobility.

Hardware Check: Periodically tighten all bolts and fasteners to prevent wobbling or instability. If any part is loose or damaged, it should be serviced or replaced as soon as possible to avoid further damage or safety risks.
Electronics: Avoid exposing the control panel and other electronic components to moisture. If the joystick or buttons become unresponsive, contact a technician for a diagnostic check.
Storage: When not in use, store the power chair in a dry, clean environment away from extreme temperatures. Covering the chair can protect it from dust and debris.
Professional Servicing: Schedule annual check-ups with a certified technician. They can perform detailed inspections, software updates, and any necessary repairs to ensure the chair's reliability.
User Manual: Always refer to the user manual provided by the manufacturer for specific care and maintenance instructions tailored to the exact model of the power chair.
Power wheelchairs provide individuals with mobility impairments the independence to navigate diverse environments. They are subject to specific accessibility and regulations designed to ensure a consistent level of accessibility to public spaces and transportation systems.
Public spaces are legally required to accommodate power wheelchairs, ensuring that individuals who use them have equal access to facilities. The Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) mandates that public spaces must have doorways that are at least 32 inches wide, ramps for any elevation change, and sufficient aisle width to allow a power wheelchair to pass. Restrooms in public venues must also have accessible stalls that accommodate these chairs. Failure to meet these standards can result in legal action against the proprietors of the public space.
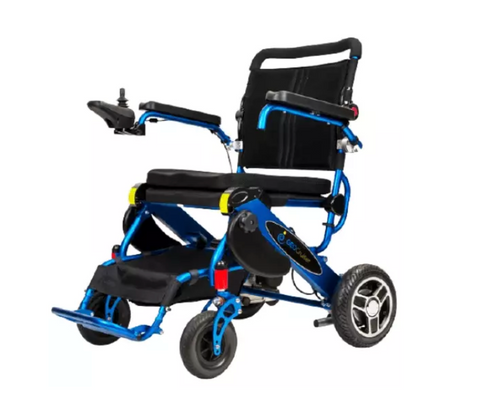

Various regulations have been put in place to ensure that power wheelchair users can travel with ease. The Department of Transportation (DOT) under the Air Carrier Access Act requires airlines to provide boarding assistance and space to stow a power wheelchair. Ground transportation such as buses and trains must also have accessible spaces and provide assistance when needed.
Both private and public transportation entities must comply with these standards to facilitate travel for power wheelchair users.
Acquiring a power wheelchair is a significant investment. It is vital for potential buyers to understand the details of insurance coverage and available assistance programs to manage the financial impact.
Medicare Part B may cover power wheelchairs as durable medical equipment (DME) if prescribed by a doctor for use in the home. A patient typically pays 20% of the Medicare-approved amount after meeting the deductible. Private insurance coverage for power wheelchairs can vary and often requires pre-approval and a copayment or co-insurance.
| Coverage Type | Document Requirements | Patient Cost Responsibility |
|---|---|---|
| Medicare Part B | Prescription, Proof of Necessity | 20% of Medicare-approved amount |
| Private Insurance | Pre-approval, Possible Copayment | Varies by Plan |
Several nonprofit organizations and state programs offer grants and funding for those who need a power wheelchair and meet specific criteria. For example:
It is crucial to research each program's specific requirements and the application process.
| Funding Source | Assistance Type | Eligibility Criteria |
|---|---|---|
| MDA | Wheelchair Funding Assistance | Diagnosis of a neuromuscular disease |
| State Programs | Employment-Related Funding | Assessment of Vocational Need |
Power chairs are transformative devices that significantly enhance the mobility and independence of individuals with physical limitations. With a variety of models and customizable features available, they cater to a wide range of needs and preferences. From offering the ability to navigate tight spaces with ease to providing comfort for extended use, power chairs are engineered to improve the quality of life for their users.
When choosing the right power chair, it is important to consider factors such as size, intended use, and control systems, as well as to seek professional assessments and hands-on trials. Proper care and maintenance are essential to ensure the longevity and optimal performance of the chair. Overall, power chairs represent a critical investment in personal mobility, offering a sense of freedom and autonomy to those who rely on them for their daily activities.
Leave a comment